Gynecological diseases in women

What types of gynecological diseases do women have?
Gynecological diseases are conditions that affect the normal function of the female reproductive organs, including the mammary glands and organs of the abdominal and pelvic region, namely the uterus (uterus), ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina and vulva.
Gynecology also includes the treatment of diseases and conditions that only women suffer from. The word comes from the French gynecologie, which is based on the Greek roots gyne – "woman" and –logy – "study".
What causes gynecological diseases?
Women's diseases are insidious diseases that can initially manifest as inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. Inflammation is often caused by certain bacteria and viruses that are infected during active sexual activity. This infection can occur from chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasmas, streptococci, staphylococci, hemophilus bacillus, candida, gonococcus, etc.
Types of women's diseases
Uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyoma or simply fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms, while others may have painful or heavy menstruation. If they are large enough, they can put pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urge to urinate. About 20% of women over the age of 30 suffer from uterine fibroids.
Menstrual disorders. Menstrual irregularities are abnormal menstrual bleeding that affects the quality of life due to irregular or excessive bleeding and may indicate certain gynecological diseases.
Endometriosis. Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system. It occurs in women and a limited number of female mammals. In endometriosis, cells similar to those of the endometrium, the layer of tissue that usually covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside it. Endometriosis occurs in a woman's body when the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium) is found in abnormal places outside the uterus, for example, in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus.
Cancers and precancerous diseases of the reproductive organs, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina and vulva. Today it is one of the most common malignant neoplasms affecting women all over the world.
Infertility. Many gynecological diseases recur several times and leave serious complications affecting reproductive health. They can even cause female infertility.
Dysmenorrhea (menstrual pain) is painful menstruation or menstrual cramps, which are pain during menstruation. Its usual onset occurs around the time when menstruation begins. Symptoms usually last less than three days. The pain is usually localized in the pelvis or lower abdomen. Secondary dysmenorrhea occurs in combination with the underlying disease of the pelvic organs. Common causes include chronic infection of the pelvic organs, endometriosis of the pelvic organs.
PCOS. Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common endocrine disease in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named because of the cysts that form on the ovaries in some people with this disease, although this is not a universal symptom and not the main cause of the disease. PCOS is the most common problem among young girls nowadays. The main culprits are stress and a sedentary lifestyle. Women with PCOS are at higher risk of developing a number of diseases, including type 2 metabolic syndrome.
Vaginitis. Vaginitis is a term used to describe any disease that causes swelling or infection of both the vulva and vagina. Trichomonas vaginitis is caused by the microorganism Trichomonas vaginalis. Suddenly, there is abundant and fetid vaginal discharge, irritation and itching.
Menopause. Menopause, also known as menopause, is the time when menstrual periods finally stop, which means the end of reproductive function. This usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact time may vary. Menopause is usually a natural change. This may happen earlier in those who smoke tobacco. After menopause, the organs of the reproductive system decrease in size; bone loss occurs by about 3-5% per year.
Neoplasm. A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive tissue growth. The process that occurs with the formation of a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of the neoplasm is not consistent with the growth of normal surrounding tissue and continues to grow abnormally, even if the initial trigger is removed.
What are the most common gynecological infections?
Some common types of gynecological infections include:
- Bacterial vaginosis.
- Candida (yeast infection).
- Chlamydia.
- Gonorrhea.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Herpes.

What is the most common gynecological problem?
Common gynecological problems include:
Cervical dysplasia.
Menstrual disorders.
Pelvic floor prolapse.
What are gynecological and genitourinary diseases?
These diseases include: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (IBD), gynecological cancers, including ovarian, cervical and endometrial cancers, uterine prolapse.
What are the most common diseases of the pelvic organs?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs or STDs) - chlamydia, mycoplasma genitalium and gonorrhea are the most common causes of STIs.
What is an acute disease in gynecology?
Acute gynecological conditions are conditions of the female reproductive system that threaten a woman's life, sexual function, or fertility. Common gynecological emergencies manifest as an acute abdomen, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or a combination of the two.
Which of the most common symptoms is a manifestation of gynecological disease?
Pain or pressure in the pelvis, different from menstrual cramps. Itching, burning, swelling, redness or soreness in the vaginal area. Ulcers or bumps in the genital area. Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant or unusual odor or unusual color.
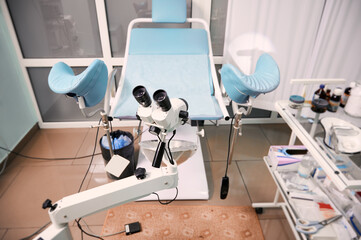
How can gynecological diseases be diagnosed?
The main diagnostic procedures include mirror examination, sonography (ultrasound), colposcopy, cervical biopsy and endocervical curettage, loop electrosurgical excision procedures, vulvar biopsy, endometrial biopsy, hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography (HSG).
What is the prevalence of gynecological diseases?
The estimated annual prevalence of the reported presence of one or more gynecological diseases was 97.1% per 1,000 women. Menstrual irregularities were the most common, with an annual prevalence rate of 53% per 1,000 women.
Why are some diseases more common in women?
Women are less susceptible to infectious diseases than men, but are more likely to develop autoimmune diseases. This higher prevalence is partly due to the X chromosome, which has many genes associated with the immune system.
How to prevent gynecological health problems?
Diet and exercise
Similarly, physical exercise can improve overall health, including the reproductive system. Maintaining a balanced weight (no higher than normal) can help with both delayed menstruation and heavy menstruation. Light exercise can help reduce any pelvic pain you may be experiencing.
Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, following hygiene rules and taking care of your sexual health can help prevent common problems such as urinary incontinence, endometriosis, pelvic organ prolapse and vaginal yeast infections.
How can we maintain our reproductive health?
Here are some simple lifestyle changes that you can make for yourself and for your loved ones in order to improve your reproductive health:
- Make love more often. Have frequent sexual intercourse, especially 5 days before and after ovulation.
- Quit smoking. Do not smoke at all: no cigarettes, no vapes, or the like.
- Exclude alcoholic beverages. Limit alcohol consumption.
- Stop drinking coffee. Reduce your caffeine intake.
- Watch out for excess weight. Maintain a healthy weight, normal for your nature depending on height.
What are the 5 ways to prevent some common reproductive problems?
Here are five steps you should take to protect your reproductive health.
- Never use aggressive cleaning and cleaning products, hygiene products.
- Wear the right underwear.
- Visit your gynecologist every year.
- Practice safe sex.
- Get tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Treatment of gynecological diseases
The treatment of various gynecological diseases is successfully carried out at the Academy of Regenerative Medicine. We use various approaches to treatment, including self-healing, natural methods (naturopathy) and an integrated approach to the body as an integral and interconnected system that functions on the basis of a proper and healthy lifestyle. In The ARM, we use only those techniques that allow you to heal not from the consequences, but from the causes of the disease. The basis of treatment is regenerative medicine, which restores, rejuvenates and awakens the cellular structure of body tissues. Self-healing is an adjustment of your body that has been knocked down as a result of external and internal influences on the body: poor ecology, poor nutrition, negative thoughts, sedentary lifestyle and negative actions towards others.
You can also heal with the help of our staff, and this is exactly cooperation for and for the benefit of your health and improving the quality of life. And you can start the processes of regeneration and recovery of the whole body! Write to us to find out more information on the topic of regenerative medicine and self-healing at the Academy of Regenerative Medicine.


